Nature Photonics 论文导读 -- 2020.06 Vol.14 Issue 6
QQ学术交流群:1092348845
详细介绍
Letters
1. 芯片级环形激光陀螺仪测量地球自转 (Earth rotation measured by a chip-scale ring laser gyroscope)
2. 可控横向轨道角动量产生时空光学涡旋 (Generation of spatiotemporal optical vortices with controllable transverse orbital angular momentum)
3. 超快、亚纳米精度和多功能飞行时间检测 (Ultrafast, sub-nanometre-precision and multifunctional time-of-flight detection)
4. 通过高度散射组织读取荧光功能信号 (Readout of fluorescence functional signals through highly scattering tissue)
5. 等离子体金纳米颗粒中的光诱导磁性 (Light-induced magnetism in plasmonic gold nanoparticles)
Articles
6. 用于芯片激光雷达反向设计的不可逆脉冲路由器 (Inverse-designed non-reciprocal pulse router for chip-based LiDAR)
7. 拉伸应变GeSn合金实现超低阈值连续和脉冲激光 (Ultra-low-threshold continuous-wave and pulsed lasing in tensile-strained GeSn alloys)
8. 无人工干预、基于深度学习的自适应微波隐身衣 (Deep-learning-enabled self-adaptive microwave cloak without human intervention)
9. 超导线性加速器驱动的MHz重复率硬X射线自由电子激光器 (A MHz-repetition-rate hard X-ray free-electron laser driven by a superconducting linear accelerator)
1. 芯片级环形激光陀螺仪测量地球自转
光学陀螺仪是最精确的转动测量设备之一,广泛用于导航和精确瞄准。自从用于通信的光子集成器件问世以来,其复杂性不断提高,人们对制备芯片级光学陀螺仪产生了兴趣。除了集成带来的潜在好处外,此类固态系统还将具有可靠、抗冲击特性。本文报道一种在硅芯片上实现的基于布里渊环形激光器的陀螺仪,其稳定性和灵敏度可以测量地球自转,这是此类新型陀螺仪的一个重要里程碑。
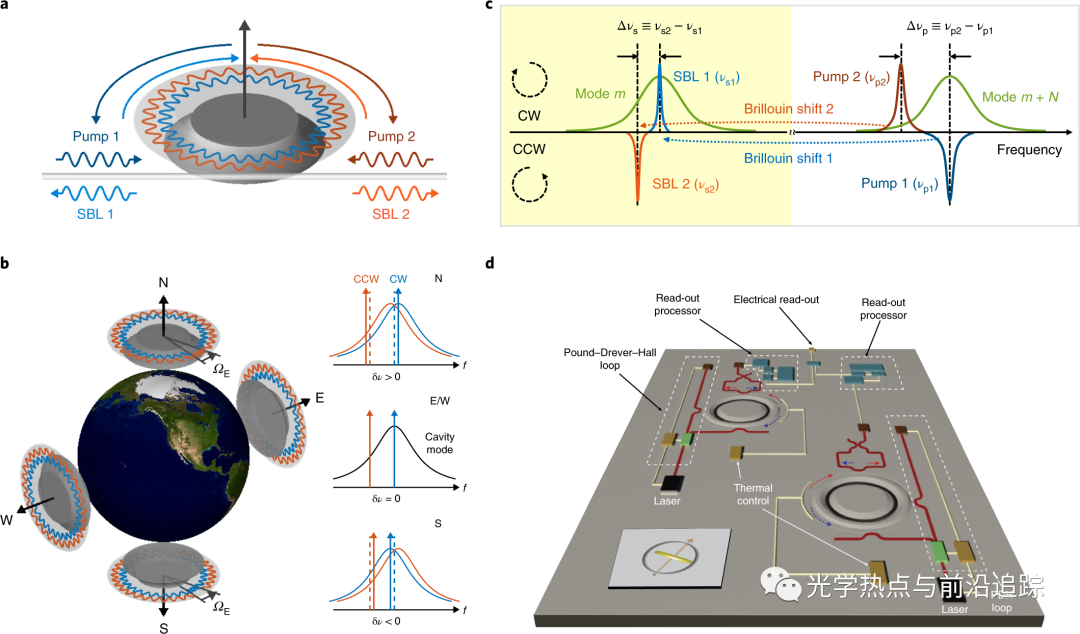
Lai, Y., Suh, M., Lu, Y. et al. Earth rotation measured by a chip-scale ring laser gyroscope. Nat. Photonics14, 345–349 (2020).
论文链接: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-020-0588-y
Optical gyroscopes are among the most accurate rotation measuring devices and are widely used for navigation and accurate pointing. Since the advent of photonic integrated components for communications, and with their increasing complexity, there has been interest in the possibility of chip-scale optical gyroscopes. Besides the potential benefits of integration, such solid-state systems would be robust and resistant to shock. Here, we report a gyroscope using Brillouin ring lasers on a silicon chip. Its stability and sensitivity enable measurement of Earth’s rotation, representing a major milestone for this new class of gyroscope.
2. 可控横向轨道角动量产生时空光学涡旋
众所周知,光具有沿传播方向的线性动量。此外,科学家还发现由于方位角相关的相位,光可以具有角动量、与圆偏振相关的自旋角动量(SAM)和与相位有关的轨道角动量(OAM)。尽管这样的角动量通常是纵向的,但垂直于传播方向的自旋角动量已经开辟了很多重要应用。然而,由于横向轨道角动量的复杂性,相关研究很少。本文演示了一种三维波包,它是一种具有可控纯横向轨道角动量的时空光学涡旋。与横向自旋角动量不同,时空涡流携带的横向轨道角动量的大小可以通过简单的调整扩展到更大值。由于时空涡流在横向的轨道角动量可控,在未来应用中具有巨大潜力。本文报道的方案可以很容易地适应其他光谱范围和不同的波场,为在较宽区域内研究和应用时空涡旋提供可能。
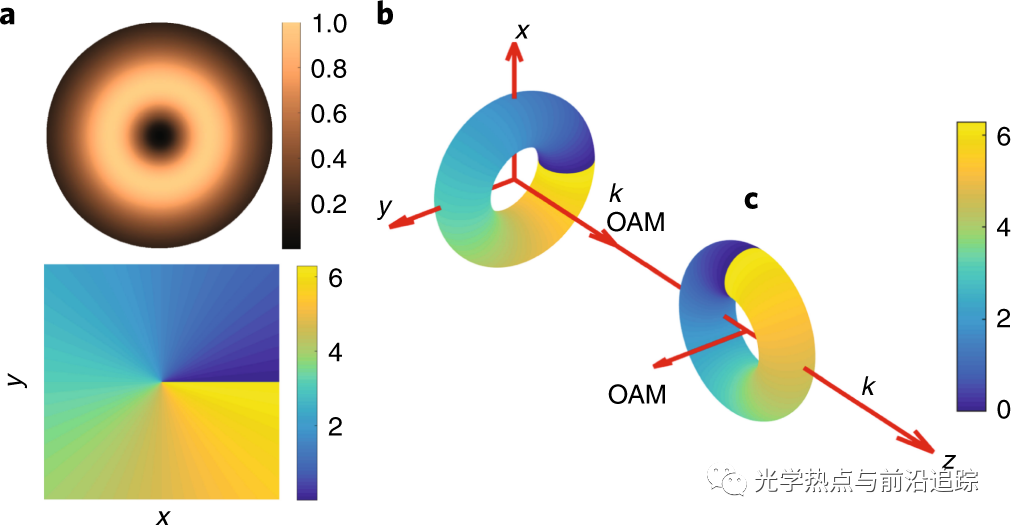
Chong, A., Wan, C., Chen, J. et al. Generation of spatiotemporal optical vortices with controllable transverse orbital angular momentum. Nat. Photonics14, 350–354 (2020).
论文链接: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-020-0587-z
Today, it is well known that light possesses a linear momentum that is along the propagation direction. Besides, scientists also discovered that light can possess an angular momentum, a spin angular momentum (SAM) associated with circular polarization and an orbital angular momentum (OAM) owing to the azimuthally dependent phase. Even though such angular momenta are longitudinal in general, an SAM transverse to the propagation direction has opened up a variety of key applications. In contrast, investigations of the transverse OAM are rare due to its complex nature. Here, we demonstrate a three-dimensional wave packet that is a spatiotemporal (ST) optical vortex with a controllable purely transverse OAM. Contrary to the transverse SAM, the magnitude of the transverse OAM carried by the ST vortex is scalable to a larger value by simple adjustments. Since the ST vortex carries a controllable OAM uniquely in the transverse dimension, it has strong potential for novel applications that may not be possible otherwise. The scheme reported here can be readily adapted for other spectral regimes and different wave fields, opening opportunities for the study and applications of ST vortices in a wide range of areas.
3. 超快、亚纳米精度和多功能飞行时间检测
位移测量是现代科技的一项基本功能。尽管已存在多种激光测距方法,在此类测量精度方面已取得了显著进步,但它们无法捕获快速和复杂的机械位移。本文建立了基于飞行时间检测的位移测量方法(通过飞秒光脉冲和锁频电子波形实现)。该方法巧妙结合了超快测量速度、亚纳米精度和毫米级非模糊量程。获得了前所未有的检测速度和精度,采集时间为4ns时,精度为24nm;采集时间为5ms时,精度可达到180pm。使用这种方法,我们展示了对单事件、快速、高动态范围的机械位移的实时检测。这种功能实现了一种新的测量和分析平台,用于实时研究宽带、瞬态和线性机械动力学,有利于实现直接探测光力学、裂纹、动态变形、非线性振动、超声现象和细胞产生。
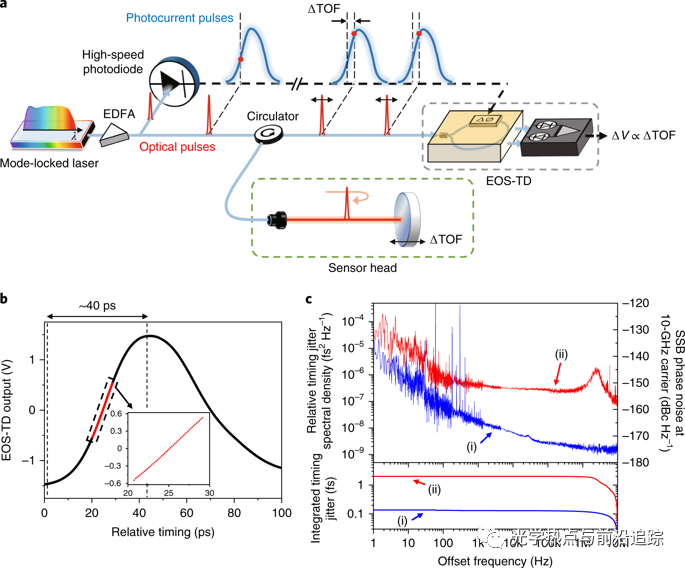
Na, Y., Jeon, C., Ahn, C. et al. Ultrafast, sub-nanometre-precision and multifunctional time-of-flight detection. Nat. Photonics14, 355–360 (2020).
论文链接: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-020-0586-0
Displacement measurement is a fundamental functionality in modern science and technology. Although there has been remarkable progress in the precision of such measurements with various laser ranging methods, they are incapable of capturing fast and complex mechanical displacements. Here, we have established a displacement measurement method using time-of-flight detection with femtosecond optical pulses and frequency-locked electrical waveforms. This method uniquely combines ultrafast measurement speed, sub-nanometre precision and non-ambiguity range of more than several millimetres. The achieved performance features unprecedented detection speed and precision. Starting from 24 nm precision for 4 ns acquisition time, the precision can reach 180 pm for 5 ms acquisition time. Using this method, we show real-time detection of single-event, fast and high-dynamic-range mechanical displacements. This capability can lead to the realization of new measurement and analysis platforms for studying broadband, transient and nonlinear mechanical dynamics in real time, which will be useful for directly probing optomechanics, the onset of cracks, dynamic deformations, nonlinear vibrations, ultrasonic phenomena and cell-generated forces.
4. 通过高度散射组织读取荧光功能信号
荧光是探测哺乳动物大脑中信息处理的有力手段。但是,神经元组织高度异质,对光不透明。用于散射光排斥、光学切片或局部激发的多种非侵入性或侵入性技术已经被提出,但是通过弹道范围之外的高度散射层的活动的非侵入性光学记录尚未实现。本文提出矩阵分解算法,从低对比度荧光斑点图案的时间序列中,得到从高度散射骨组织下方产生的荧光时变源功能信号。
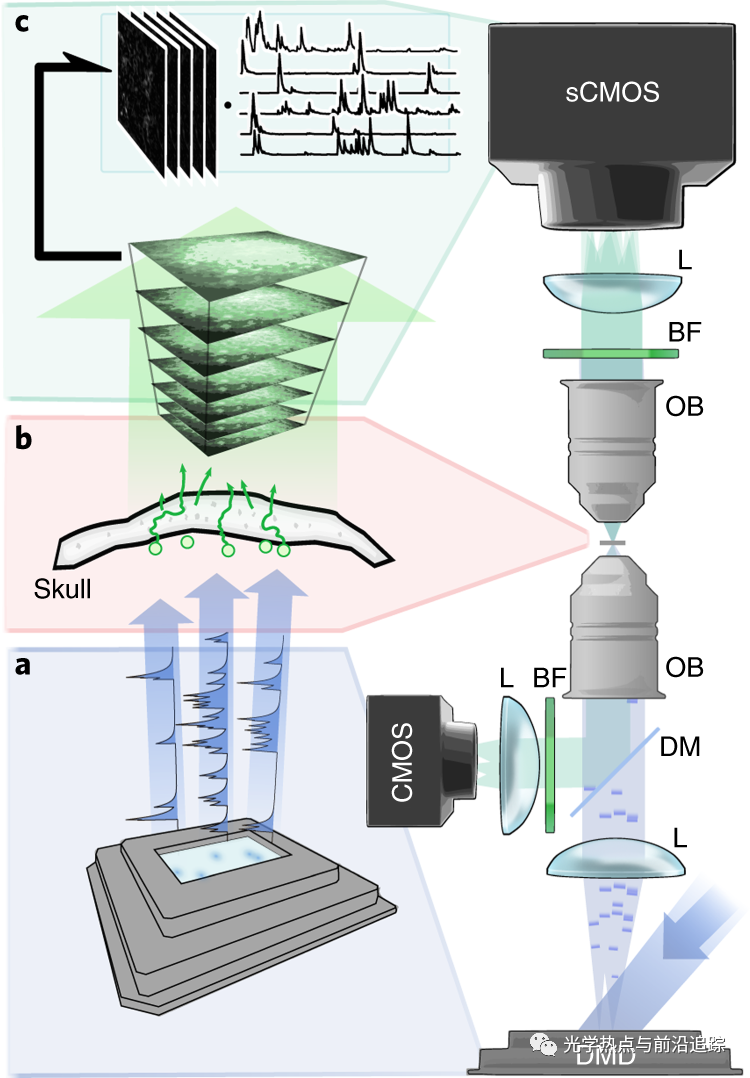
Moretti, C., Gigan, S. Readout of fluorescence functional signals through highly scattering tissue. Nat. Photonics14, 361–364 (2020).
论文链接: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-020-0612-2
Fluorescence is a powerful means to probe information processing in the mammalian brain. However, neuronal tissues are highly heterogeneous and thus opaque to light. A wide set of non-invasive or invasive techniques for scattered light rejection, optical sectioning or localized excitation have been developed, but non-invasive optical recording of activity through a highly scattering layer beyond the ballistic regime is impossible as yet. Here, we show that functional signals from fluorescent time-varying sources located below a highly scattering bone tissue can be retrieved efficiently by exploiting matrix factorization algorithms to demix this information from temporal sequences of low-contrast fluorescence speckle patterns.
5. 等离子体金纳米颗粒中的光诱导磁性
由于对磁存储器、自旋电子、量子计算等技术的潜在影响、以及光隔离和不可逆等应用中进行非线性光学控制和调制的可能性,超快光学磁控制方法一直是数十年来研究的热点。本文报道了在等离激元金纳米颗粒中的光诱导磁化强度实验量化结果(与法拉第逆效应有关)。在典型的超快脉冲激励(<1014 W m-2峰值强度)下,感应磁矩很大,其磁化和消磁在亚皮秒时间分辨率内是瞬时的。研究结果支持了角动量从光场到电子气的相干传递机制,并为不需要外部施加磁场的全光亚波长光隔离方法开辟了途径。
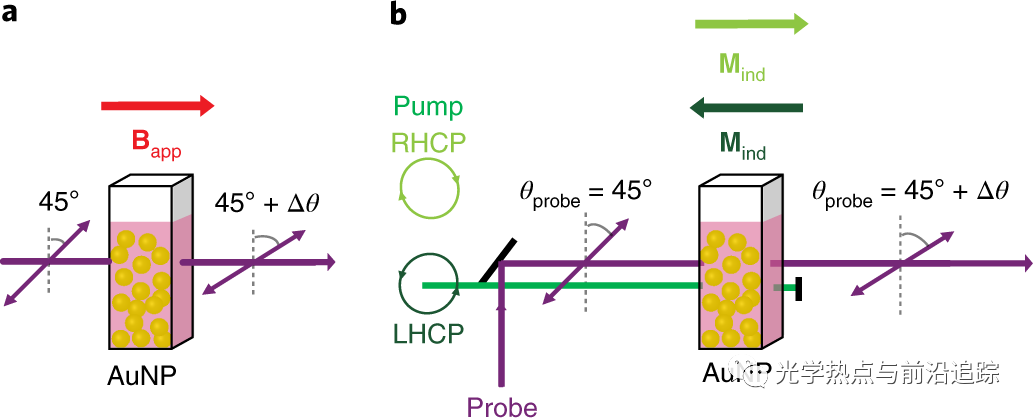
Cheng, O.H., Son, D.H. & Sheldon, M. Light-induced magnetism in plasmonic gold nanoparticles. Nat. Photonics14, 365–368 (2020).
论文链接: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-020-0603-3
Strategies for the ultrafast optical control of magnetism have been a topic of intense research for several decades because of the potential impact in technologies such as magnetic memory, spintronics and quantum computation, as well as the opportunities for nonlinear optical control and modulation in applications such as optical isolation and non-reciprocity. Here we report experimental quantification of optically induced magnetization in plasmonic gold nanoparticles due to the inverse Faraday effect. The induced magnetic moment is large under typical ultrafast pulse excitation (<1014 W m−2 peak intensity), with magnetization and demagnetization kinetics that are instantaneous within the subpicosecond time resolution of our study. Our results support a mechanism of coherent transfer of angular momentum from the optical field to the electron gas, and open the door to all-optical subwavelength strategies for optical isolation that do not require externally applied magnetic fields.
6. 用于芯片激光雷达反向设计的不可逆脉冲路由器
不可逆设备,如隔离器和循环器,是微波和光频通信系统的关键技术。尽管基于电磁效应的不可逆设备已经应用于自由空间和光纤通信系统,但它们的芯片化一直面临挑战,主要是由于随之而来的高插入损耗,弱磁光效应和材料不兼容问题。我们发现,χ(3)非线性谐振器可实现全无源、低损耗、无偏置非互易传输,可用于光学系统,如芯片激光雷达。一种多端口非线性Fano谐振器被用于在基于频率梳的光学测距中的芯片不可逆脉冲路由器。由于时间反转对称性对单个非线性谐振器的功率范围和传输施加了严格限制,因此我们实现了级联的Fano-Lorentzian谐振器系统,该系统克服了这些限制,并显著改善了当前最先进的设备插入损耗和功率范围,为单向传输和路由提供了独立于平台的设计,非常适合光子集成。
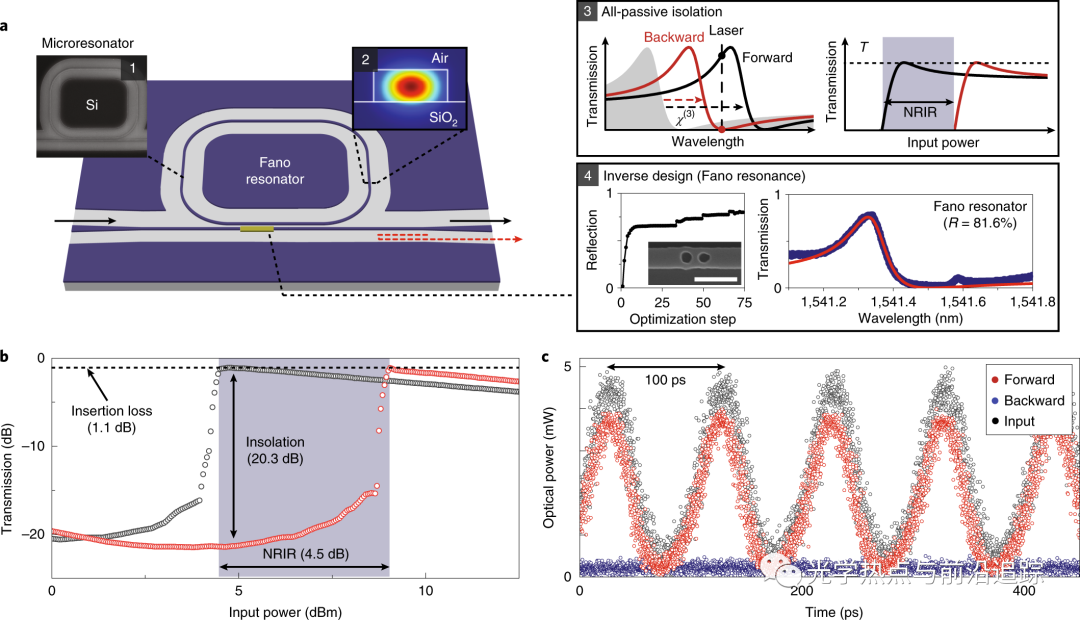
Yang, K.Y., Skarda, J., Cotrufo, M. et al. Inverse-designed non-reciprocal pulse router for chip-based LiDAR. Nat. Photonics14, 369–374 (2020).
论文链接: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-020-0606-0
Non-reciprocal devices such as isolators and circulators are key enabling technologies for communication systems, both at microwave and optical frequencies. Although non-reciprocal devices based on magnetic effects are available for free-space and fibre-optic communication systems, their on-chip integration has been challenging, primarily due to the concomitant high insertion loss, weak magneto-optical effects and material incompatibility. We show that χ(3)nonlinear resonators can be used to achieve all-passive, low-loss, bias-free non-reciprocal transmission for applications in photonic systems such as chip-scale LiDAR. A multi-port nonlinear Fano resonator is used as an on-chip, non-reciprocal pulse router for frequency comb-based optical ranging. Because time-reversal symmetry imposes stringent limitations on the operating power range and transmission of a single nonlinear resonator, we implement a cascaded Fano–Lorentzian resonator system that overcomes these limitations and substantially improves the insertion loss and operating power range of current state-of-the-art devices. This work provides a platform-independent design for non-reciprocal transmission and routing that is ideally suited for photonic integration.
7. 拉伸应变GeSn合金实现超低阈值连续和脉冲激光
应变GeSn合金有望实现基于IV族元素的发光体。本文采用SiNx应力源层封装的GeSn微碟激光器产生拉伸应变。300纳米厚的GeSn层和原子百分比5.4%的Sn(间接带隙半导体)通过拉伸应变技术转变为支持激光的直接带隙半导体。在这种方法中,低浓度的Sn可改善缺陷,并且拉伸应变在价带边缘(即轻空穴带)传递低密度状态。我们分别在高达70 K和100 K的温度下观察到超低阈值连续激光和脉冲激光。波长为2.5μm激光器的纳秒脉冲光激发阈值为0.8 kW cm-2,连续光激发阈值为1.1 kW cm-2。该结果为硅光子平台单片集成IV族激光源提供了一种可能。
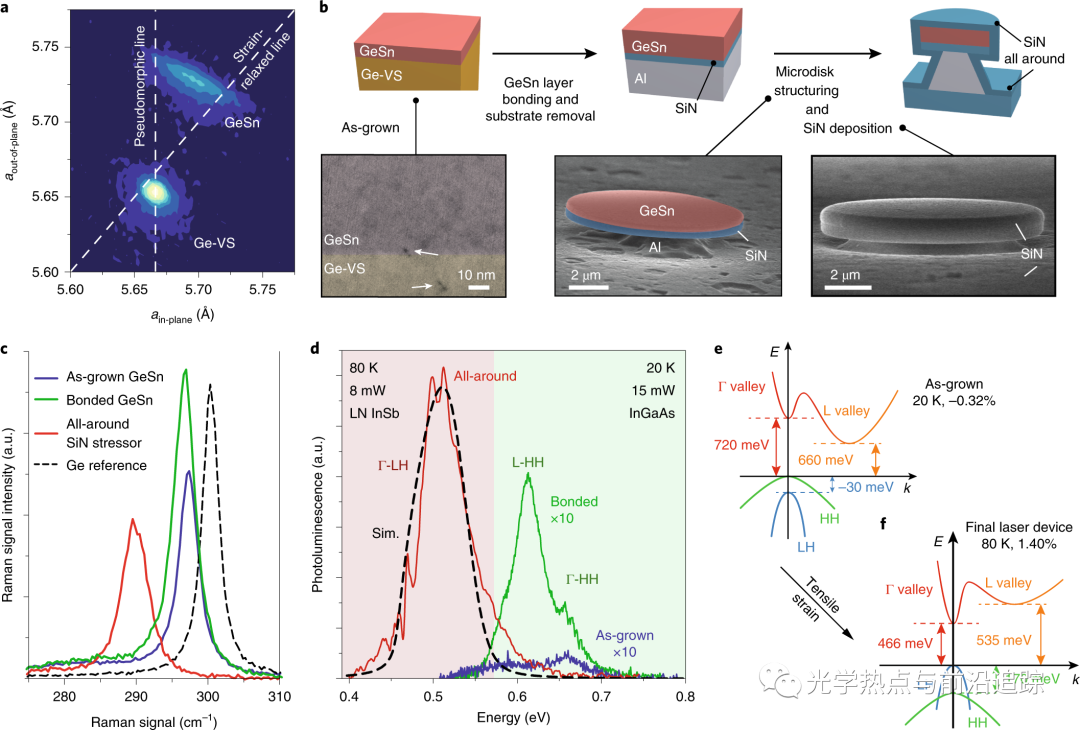
Elbaz, A., Buca, D., von den Driesch, N. et al. Ultra-low-threshold continuous-wave and pulsed lasing in tensile-strained GeSn alloys. Nat. Photonics14, 375–382 (2020).
论文链接: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-020-0601-5
Strained GeSn alloys are promising for realizing light emitters based entirely on group IV elements. Here, we report GeSn microdisk lasers encapsulated with a SiNx stressor layer to produce tensile strain. A 300 nm-thick GeSn layer with 5.4 at% Sn, which is an indirect-bandgap semiconductor as-grown, is transformed via tensile strain engineering into a direct-bandgap semiconductor that supports lasing. In this approach, the low Sn concentration enables improved defect engineering and the tensile strain delivers a low density of states at the valence band edge, which is the light hole band. We observe ultra-low-threshold continuous-wave and pulsed lasing at temperatures up to 70 K and 100 K, respectively. Lasers operating at a wavelength of 2.5 μm have thresholds of 0.8 kW cm−2 for nanosecond pulsed optical excitation and 1.1 kW cm−2 under continuous-wave optical excitation. The results offer a path towards monolithically integrated group IV laser sources on a Si photonics platform.
8. 无人工干预、基于深度学习的自适应微波隐身衣
人类为实现隐形而着迷了几个世纪,近十年,超材料的出现引起了广泛关注。但是,目前最先进的隐形斗篷通常工作在确定性系统中,或在外部配合下实现主动隐形。本文提出由深度学习驱动的智能(即自适应)隐身衣概念,并以超表面隐身衣作为实施示例。实验中,超表面隐身衣对不断变化的入射波和周围环境表现出毫秒响应时间,期间不需要人工干预。该工作提供了一种接近于实时的隐身方案,可应用于移动隐形车等。该方法为促进微波范围内以及更宽电磁频谱内的其他智能设备开辟了道路,更普遍地讲,使电磁逆设计问题的自动方案成为现实。
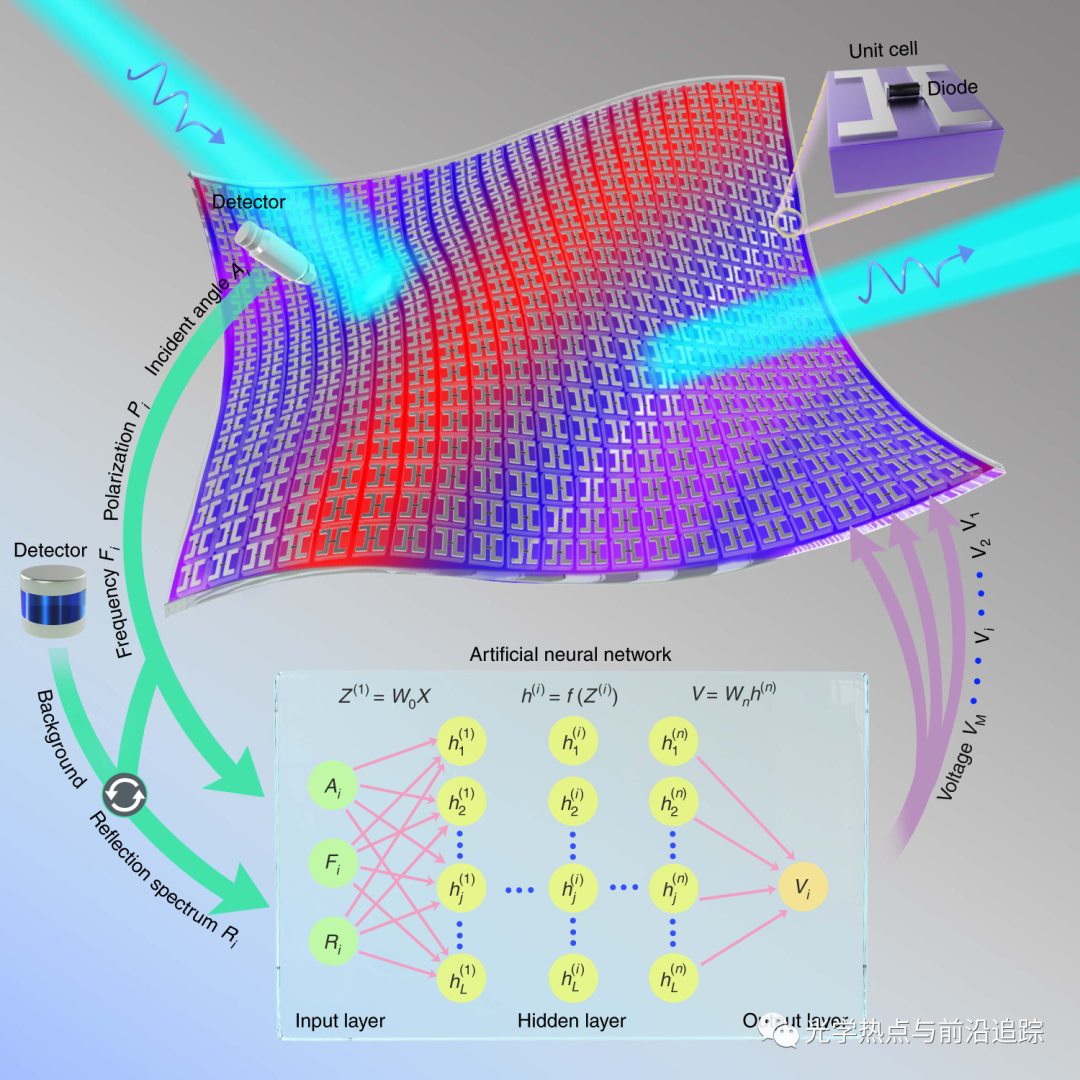
Qian, C., Zheng, B., Shen, Y. et al. Deep-learning-enabled self-adaptive microwave cloak without human intervention. Nat. Photonics14, 383–390 (2020).
论文链接: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-020-0604-2
Becoming invisible at will has fascinated humanity for centuries and in the past decade it has attracted a great deal of attention owing to the advent of metamaterials. However, state-of-the-art invisibility cloaks typically work in a deterministic system or in conjunction with outside help to achieve active cloaking. Here, we propose the concept of an intelligent (that is, self-adaptive) cloak driven by deep learning and present a metasurface cloak as an example implementation. In the experiment, the metasurface cloak exhibits a millisecond response time to an ever-changing incident wave and the surrounding environment, without any human intervention. Our work brings the available cloaking strategies closer to a wide range of real-time, in situ applications, such as moving stealth vehicles. The approach opens the way to facilitating other intelligent metadevices in the microwave regime and across the wider electromagnetic spectrum and, more generally, enables automatic solutions of electromagnetic inverse design problems.
9. 超导线性加速器驱动的MHz重复率硬X射线自由电子激光器
欧洲X射线自由电子激光器(XFEL)是基于高能电子超导线性加速器的硬X射线自由电子激光(FEL)。超导技术允许在加速电压的一个射频脉冲内加速许多电子束,进而产生大量的硬X射线脉冲。本文报道了欧洲XFEL加速器的性能,该加速器每秒加速超过5000个电子束,并具有17.5 GeV的满程能量。反馈机制使FEL波动器在空间和时间上的电子束传输稳定。在9.3 keV处测得的FEL增益曲线与预测的饱和FEL辐射非常吻合。在7 keV和14 keV之间实现了硬X射线脉冲能量高达2.0 mJ。使用高重复率时,FEL光束平均功率为6 W。
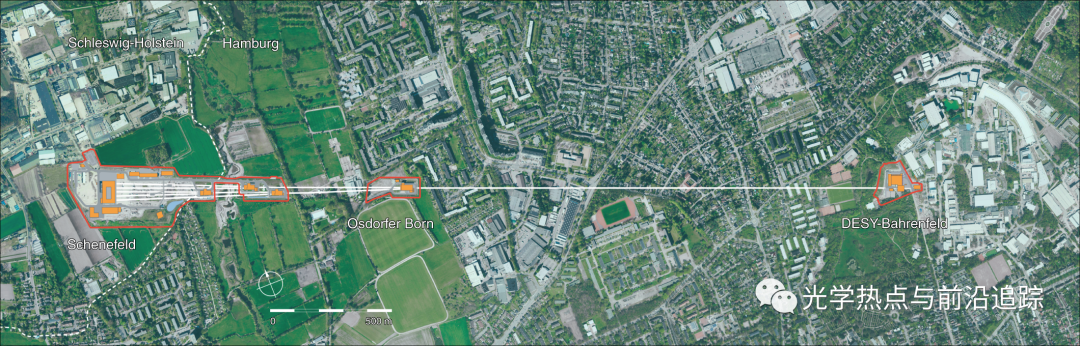
Decking, W., Abeghyan, S., Abramian, P. et al.A MHz-repetition-rate hard X-ray free-electron laser driven by a superconducting linear accelerator. Nat. Photonics14, 391–397 (2020).
论文链接: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-020-0607-z
The European XFEL is a hard X-ray free-electron laser (FEL) based on a high-electron-energy superconducting linear accelerator. The superconducting technology allows for the acceleration of many electron bunches within one radio-frequency pulse of the accelerating voltage and, in turn, for the generation of a large number of hard X-ray pulses. We report on the performance of the European XFEL accelerator with up to 5,000 electron bunches per second and demonstrating a full energy of 17.5 GeV. Feedback mechanisms enable stabilization of the electron beam delivery at the FEL undulator in space and time. The measured FEL gain curve at 9.3 keV is in good agreement with predictions for saturated FEL radiation. Hard X-ray lasing was achieved between 7 keV and 14 keV with pulse energies of up to 2.0 mJ. Using the high repetition rate, an FEL beam with 6 W average power was created.
- 上一款: 碳纳米管为人的肺部疾病分析铺平道路
- 下一款: Nature Nano:纳米“线”递送miR

 公司简介
公司简介