Advanced Science | Caspase-3/GSDME-mediated trophoblast pyroptosis and reciprocal macrophage polarization lead to early-onset preeclampsia inflammation
QQ Academic Group: 1092348845
Detailed
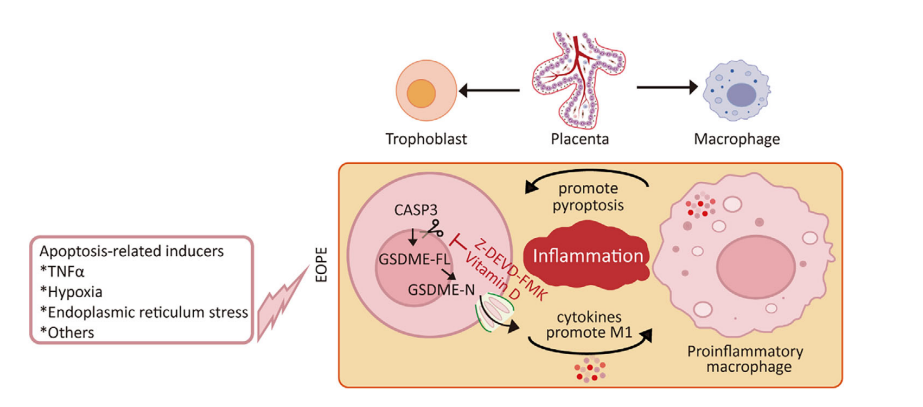
Early-onset preeclampsia (EOPE) is associated with excessive apoptosis and inflammation, but the mechanistic links between these processes remain a mystery. This study reports that circulating pro-apoptotic proteins are elevated in the early pregnancy of EOPE patients, while EOPE placentas show CASP3 activation and GSDME cleavage. Using multiple trophoblast cell lines, we demonstrate that trophoblasts with high GSDME expression switch from apoptosis to CASP3-dependent pyroptosis.thus driving inflammation. Notably, trophoblast cells further induce pro-inflammatory macrophage polarization within placental villous organoids, establishing a feedback loop that enhances trophoblast pyroptosis and inflammatory responses in the trophoblast-macrophage assembly. In vivo, CASP3-GSDME-mediated trophoblast pyroptosis induces systemic inflammation in wild-type pregnant mice,But this effect was not observed in Gsdme −/− mice. Screening for preventive drugs for EOPE showed that vitamin D is an inhibitor of GSDME activation and pyroptosis in trophoblast cells. Our joint research results establish that CASP3–GSDME-mediated gradual reduction serves as a mechanistic link between apoptosis and inflammation in EOPE.

In the complex pathological mechanisms of early-onset preeclampsia (EOPE), the connection between apoptosis and inflammation has not been clearly elucidated. Recently, a study systematically analyzed clinical samples, various trophoblast models, and animal experiments, revealing that CASP3/GSDME-mediated trophoblast pyroptosis and its interaction with macrophage polarization constitute a key molecular loop driving placental and systemic inflammation in EOPE.
References:
DOI: 10.1002/advs.202516948
- Previous: ACS Nano | Heterogeneo
- Next: IF: 20.3! New Breakthr

 Academic Frontier
Academic Frontier