

Hydrogels have recently received a lot of attention due to their potential in many applications, such as human-machine interfaces, sensors, actuators, and flexible energy storage. Thanks to its hydrophilicity, metal conductivity, high aspect ratio morphology and wide controllable properties, when two-dimensional (2D) transition metal carbides/nitrides (MXenes) are incorporated into the hydrogel system, Can provide satisfactory controllable specific application performance. Some properties of MXene hydrogel are affected by the complex gel structure and gelation mechanism, which requires researchers to conduct in-depth research and engineering design on the nanoscale. On the other hand, preparing MXene into a hydrogel can significantly improve the stability of MXene, which is usually a limiting factor for many MXene-based applications. In addition, through simple processing, hydrogel derivatives of MXene, such as aerogels, can be obtained, thereby further expanding its functional diversity. Recently, Professor Husam N. Alshareef of King Abdullah University of Science and Technology in Saudi Arabia published a review article titled: MXene hydrogels: fundamentals and applications in the top international review journal Chem Soc Rev, summarizing the differences of various MXene-based hydrogel systems Structure, gelation mechanism and corresponding driving force.

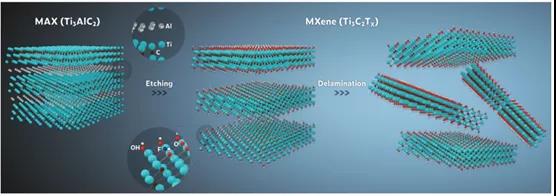
Figure 1. The general assembly strategy of Ti3C2TxMXene.
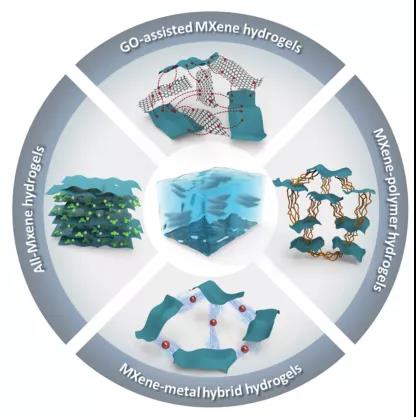
Figure 2. Summary of MXene-based hydrogels.
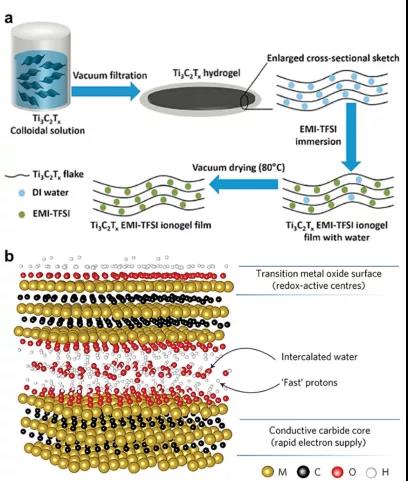
Figure 3. Preparation process of full MXene hydrogel and ionic gel.
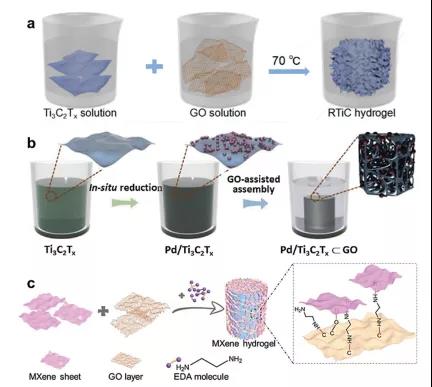
Figure 4. The synthesis process of different MXene hydrogels assisted by GO.
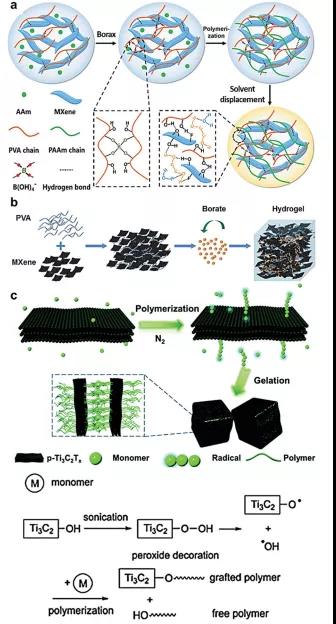
Figure 5. Synthesis process of polymer-based MXene hydrogel.
Figure 6. The gelation process of metal ions and MXene nanosheets.

Figure 7. Schematic diagram of the synthesis process of MXene aerogel.
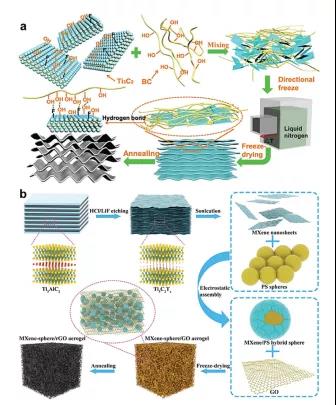
Figure 8. Synthesis process of MXene-based composite materials.
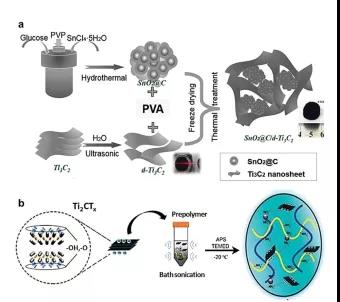
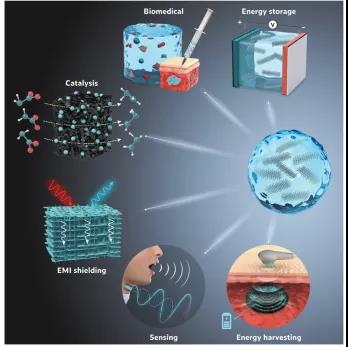
Figure 9. Potential applications of MXene hydrogel and its derivatives.
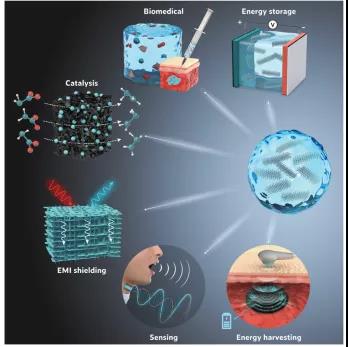
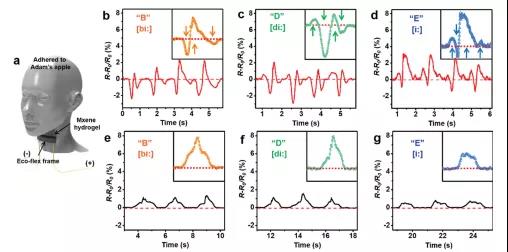
Figure 12. MXene-PVA hydrogel is used for sensing applications.
This article summarizes the research progress of MXene-based hydrogels. Generally, an important property of gel chemistry is that small changes in interacting components can easily lead to diversification of functions; in principle, similar to other hydrogels, based on MXene The gelation of the hydrogel includes covalent and non-covalent crosslinking methods; due to the lack of research on basic issues, such as the mass/charge transfer between MXene nanosheets and other components in the hydrogel system, The kinetics/thermodynamics of the assembly process and the mechanism of the interaction between the components; currently existing devices based on MXene hydrogels are artificially prepared, staying at the laboratory level, and difficult to replicate or mass-produce. This is also the future Researchers need to focus on the direction.
Literature link:
DOI: 10.1039/d0cs00022a
Information source: MXene Frontie
This information is from the Internet for academic exchanges. If there is any infringement, please contact us and delete it immediately

















