
Hydrogel is similar to biological soft tissue, with unique microenvironment (high water content and permeability) and self-adaptive characteristics. It has shown great application potential in the fields of drug sustained release, wound dressing, tissue engineering and flexible electronic devices. . However, the mechanical properties and swelling resistance of traditional hydrogels are usually poor, which limits their practical applications.
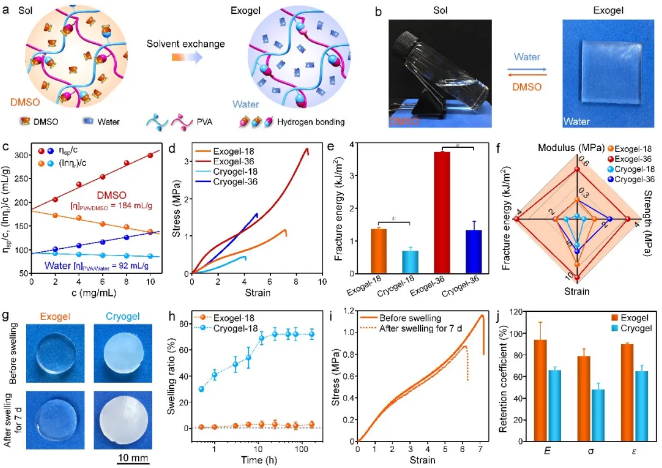
With the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the research team of Professor Qiu Dong from the Polymer Physics and Chemistry Laboratory of the Institute of Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has been committed to the development and functionalization of strong hydrogels in recent years, and has made a series of progress. Recently, Qiu Dong research group and Qiao Yan research group have cooperated, from the perspective of regulating the interaction between polymer chains, and proposed a strategy for adjusting the time-domain expression of non-covalent interactions through solvent replacement to optimize the structure of polymer crosslinking networks. , And successfully used to prepare anti-swelling and tough hydrogels (exogels). The principle of this strategy is: in a good solvent, the non-covalent interactions within/between polymer chains are inhibited, which helps the polymer chains maintain a stretched conformation and uniform distribution; after being replaced with a poor solvent, the polymer chains The non-covalent interaction between them can be maximized to restore, thereby increasing the density and uniformity of cross-linking points. Using dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)-water solvent pair, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) exogels were prepared through time-domain control of hydrogen bonds, and its mechanical properties and swelling resistance were significantly better than those prepared by the classic freeze-thaw method. Glue (PVA cryogels). At the same time, the solution-gel transition driven by water as the terminal solvent gives PVA exogels good underwater bonding ability.
Relevant research results were published in the recent Advanced Materials magazine under the title A Solvent-Exchange Strategy to Regulate Noncovalent Interactions for Strong and Antiswelling Hydrogels and selected as the Back Cover of the current issue. The corresponding authors are Researcher Qiu Dong and Researcher Qiao Yan, and the first author is Dr. Xu Liju.
Paper link:
DOI: 10.1002/adma.202004579.
Information source: Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences
This information is from the Internet for academic exchanges. If there is any infringement, please contact us and delete it immediately






