已传文件:photo/1766544328.png
Featured Article
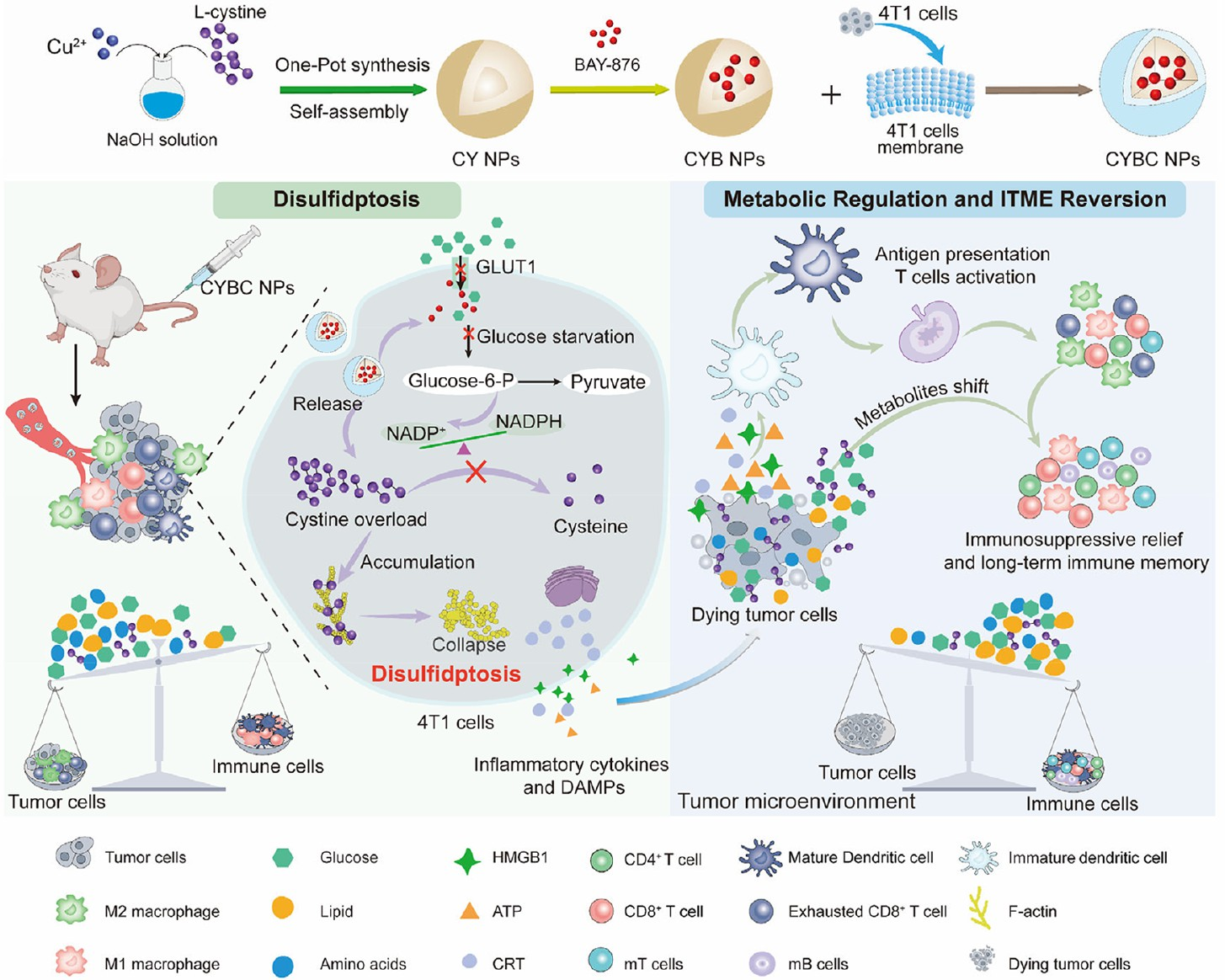
Malignant tumor metabolic reprogramming drives proliferation and immune evasion by hijacking essential nutrients and shaping an immunosuppressive microenvironment. Although targeting tumor metabolism offers therapeutic prospects, selectively modulating abnormal metabolic pathways without affecting normal cells remains a significant challenge. Disulfidation is a recently discovered form of metabolism-dependent regulated cell death that may provide a route for metabolic disruption; however, its immunoregulatory potential has yet to be explored.This study designed a disulfide-containing nano-inducer (CYBC NPs), a nanoplatform co-loading cystine and the GLUT1 inhibitor BAY-876, camouflaged with a cancer cell membrane, which selectively induces disulfide stress in triple-negative breast cancer cells. By simultaneously blocking glucose uptake and supplying cystine, CYBC NPs trigger disulfide-mediated cytoskeletal collapse, reprogram tumor metabolic flux, and induce immunogenic cell death. This metabolic perturbation promotes dendritic cell maturation, M1-like macrophage polarization, and activation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes.Thus, ITME is reversed and tumor growth is suppressed. Notably, CYBC NPs trigger a strong, non-exhausted anti-tumor immune response and generate lasting immune memory, effectively preventing tumor recurrence and metastasis. In summary, our study demonstrates the implementation of disulfide as an independent immunotherapy strategy, providing a paradigm shift for metabolism-driven cancer immunotherapy.
Original link
Disulfidptosis Nanoinducer Interrupts Tumor Metabolic Privilege to Boost Sustained Immunotherapy
ACS Nano ( IF 16 )
Pub Date : 2025-08-11
DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.5c08432
Yapeng Xu, Xiaoqi Ming, Jinxiu Qi, Zhenqiu Huang, Hongling Zhu, Mingyu Wu, Shun Feng, Yu Wan




