已传文件:photo/1766544328.png
Featured Article
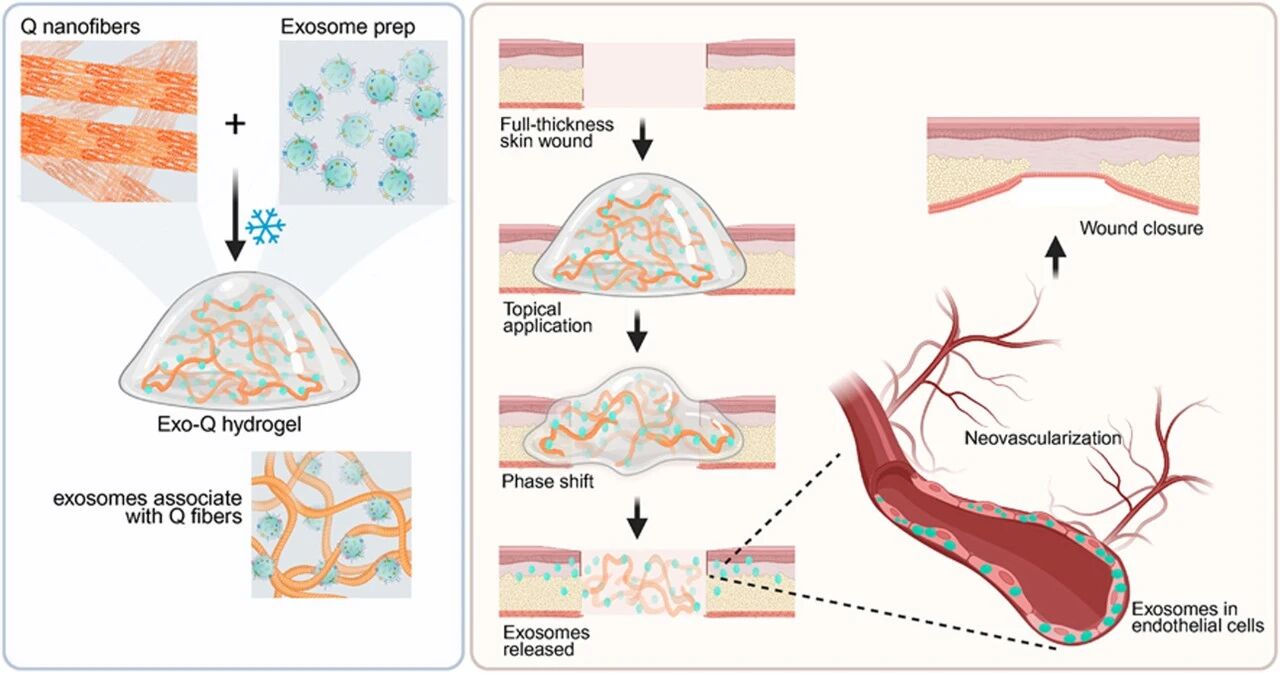
Chronic wounds, especially in diabetic patients, pose significant clinical challenges due to microvascular damage and delayed healing. This study introduces Exo-Q, a novel thermoresponsive hydrogel formed by co-gelation of engineered Q protein nanofibers and a class of vesicular intercellular communication mediators called exosomes. Exo-Q transitions from a gel to a viscoelastic solution at physiological temperature, enabling localized exosome delivery with an initial burst release followed by sustained release. In a diabetic mouse wound model, Exo-Q effectively delivered exosomes derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells directly to the wound bed, where these exosomes accumulated in the endothelial cells of the granulation tissue.And no detectable systemic distribution. Exosomes produced under strict and reproducible cell culture conditions consistently carry biomolecular cargo rich in miRNAs, which have been validated to target angiogenesis-related genes, demonstrating their therapeutic potential. Topical Exo-Q results in extensive formation of neovascularized granulation tissue, significantly accelerating wound closure to levels comparable to non-diabetic wounds. Importantly, the modular design of the hydrogel maintains the functional integrity of both Q protein nanofibers and exosomes.It demonstrates compatibility with full-thickness human wounds. This platform allows for personalized customization, tailored to the critical stages of diabetic wound healing, while ensuring efficacy at low doses, with the potential for patient self-treatment. By leveraging advanced biomaterials, Exo-Q enhances the effectiveness of exosome-based interventions for diabetic wounds, offering a localized, non-invasive solution for chronic and hard-to-heal wounds. This innovative hydrogel platform represents a modular therapeutic strategy with great potential for clinical applications in regenerative medicine.
Original link
Duo-nano exosome encapsulating hydrogel boosts wound healing across xenogenic and allogenic models
Biomaterials ( IF 12.9 )
Pub Date : 2026-01-03
DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2025.123975
Bibi S. Subhan, Sydney Hanson, Dianny Almanzar, Juan F. Cortes Troncoso, Priya Katyal, Jonathan W. Sun, Hao-Wei Shih, Tamara Mestvirishvili, Michael Meleties, Fernando Arias, Andrew Wang, Kelly Ruggles, Igor Dolgalev, Paolo Mita, Jin Kim Montclare, Piul S. Rabbani




