MXenes has a wide range of applications in many fields such as energy storage and conversion, photocatalysis, water deionization, electromagnetic shielding, biosensors, etc. Recently, it was also investigated MXenes at relatively high temperatures ( ~ 550 O C) catalytic applications under. However, it has not yet been reported to involve a higher temperature ( ≥ 600 O C) and a high concentration of the oxidant (40% carbon dioxide ) severe conditions like MXenes based catalyst.
Achievements
Recently, Auburn University ‘s Carlos A. Carrero professor in the top international journal ACS Catalysis published entitled " Insights at The Genesis of INTO A Selective and Coke-Resistant MXene for the Catalyst Based at The Dry Reforming of Methane " papers. We report a multi-layer V 2 CT x MXene (mV 2 CT x ) as a precursor for the catalysis of carbon oxides, which converts CH 4 and carbon dioxide into synthesis gas through methane dry gas reforming (DRM) . The V 2 O 3 −V 8 C 7 / mV 2 CT x catalyst generated in situ undergoes a redox mechanism, exhibits high reactivity and selectivity, and is unprecedentedly stable. V2O3 and V8C7 grown in situ modified mV 2 CT x to make better use of the V site, thus making VThe activity of 2 O 3 −V 8 C 7 / mV 2 CT x catalyst is four times higher than that of V 2 AlC MAX phase and commercial vanadium carbide (VC).

Figure 1 Structure of mV 2 CT x MXene .

Figure 2 Structure and morphology of V 2 AlC and mV 2 CT x MXene .

Figure 3 Conversion rates of CH 4 and carbon dioxide.

Figure 4 CH 4 and carbon dioxide conversion activity.

Figure 5 Comparison of CH 4 conversion of various catalysts .

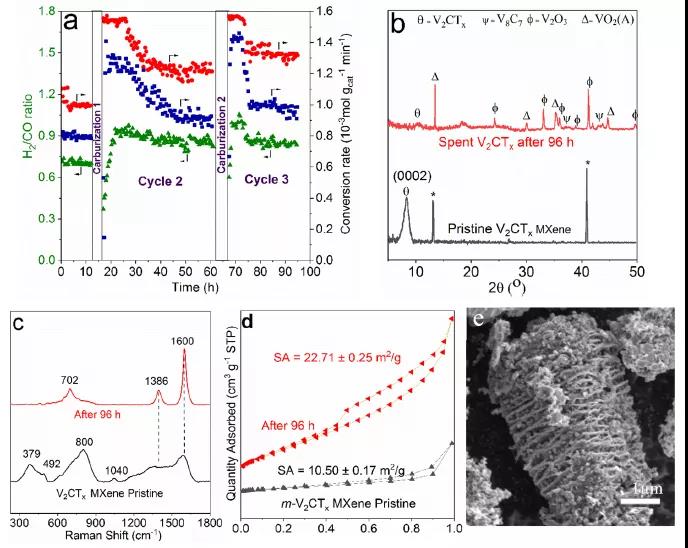
Figure 6 Conversion of CH 4 and carbon dioxide after carburization .

Figure 7 DRM response within 5.5 h .

Figure 8 DRM reaction mechanism.
in conclusion
Spectroscopy, and isotope labeling experiments microscopy results show that the original mV 2 CT X during dehydration, produces oxide / carbide (V 2 O . 3 -V . 8 C . 7 / mV 2 CT X ) , further In the presence of CO 2 , additional V2O3 nanocrystals are generated between the surface and the multilayer structure . These oxide particles react with CH 4 and are further carbonized in situ to transform into V 8 C 7 nanocrystals. This study provides insight into the dynamics, structure, and mechanics of mV 2 CT x as a DRM selectivity and the origin of anti-carbon deposition catalysts. mV 2 CT x and MXenes at relatively high temperatures( ≥ 500 o C) It has broad application prospects as a precursor, carrier and catalyst.
Original link:
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acscatal.0c00797
Source: MXene Academic












