
The significant increase in CO 2 emissions and the continued acceleration of the loss of fossil fuels have caused serious global warming and fuel shortages. Photocatalysis is considered to be an effective method to solve this problem. Among the photocatalysts, titanium dioxide (TiO 2 ) is given high hopes due to its chemical stability, environmental friendliness, and abundant resources. However, the single-component photocatalyst is limited because it is difficult to balance the strong redox ability and the wide light response range.
Achievements
Recently, Wuhan University of Yu Jiaguo professor at Hong Kong University education of Wingkei Ho professor and Jagiellonian University of Wojciech Macyk professor in the top international journal Applied Catalysis B: Environmental published entitled " 2D / 2D / 0D TiO 2 / C 3 N 4 / Ti 3 C 2 MXene composite S-scheme photocatalyst with enhanced CO 2 reduction activity ” paper. Preparation of 2D / 2D Van der Waals heterojunction ( titanium dioxide) of core-shell structure by in-situ growth of C 3 N 4 layer on two-dimensional (2D) TiO 2 mesoporous nanosheets/ C 3 N 4 ) , and then zero-dimensional (0D) Ti 3 C 2 MXene quantum dots (TCQD) are distributed on the surface of C 3 N 4 by electrostatic action . Compared with TiO 2 , C 3 N 4 , TiO 2 / C 3 N 4 and C 3 N 4 / Ti 3 C 2 , the 2D / 2D / 0D TiO 2 / C 3 N 4 / Ti 3 C 2 composite Nodules in CO andThe preparation of CH4 showed stronger CO 2 reduction activity. X -ray photoelectron spectroscopy and electron paramagnetic resonance analysis show that the reduction of CO 2 is mainly a segmented charge transfer mechanism. This work provides a reasonable structural design for the regulation of the number and type of heterojunctions, and further understands the mechanism of multi-junction photocatalysts.

Figure 1 Schematic diagram of preparation of TCQD modified TiO 2 / C 3 N 4 core-shell nanosheets.
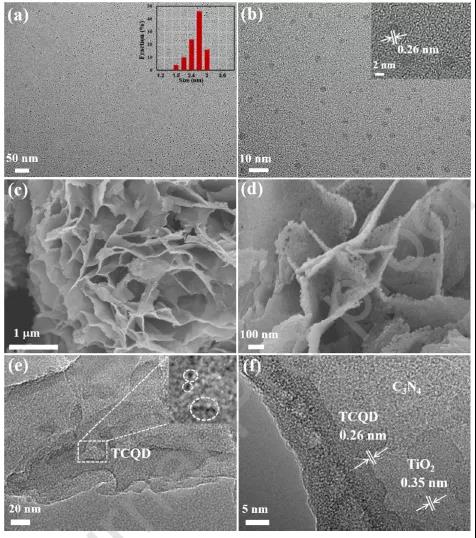

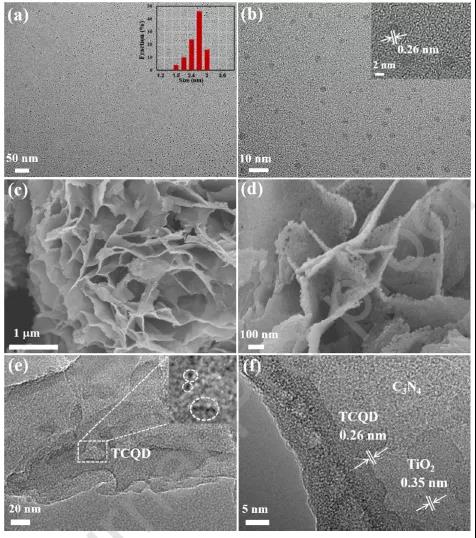
FIG 2 TCQD modified Ti02 2 / C . 3 N . 4 morphology of core-shell nano sheet.
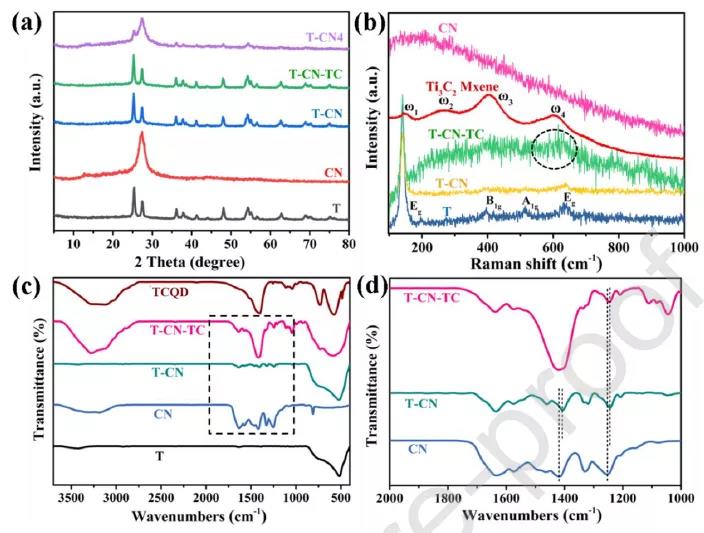
Figure 3 The crystal form of TCQD modified TiO 2 / C 3 N 4 core-shell nanosheets.
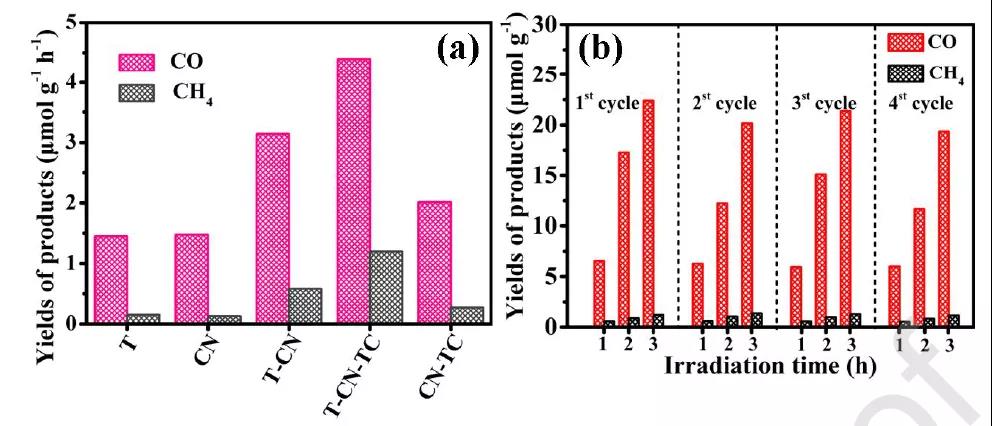
Figure 4 The photocatalytic CO 2 reduction performance of the prepared samples .
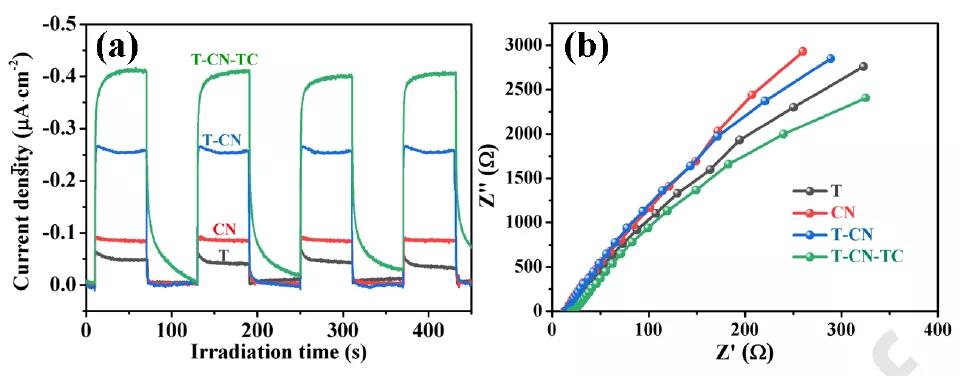
Figure 5 Transient photocurrent response and EIS spectrum.
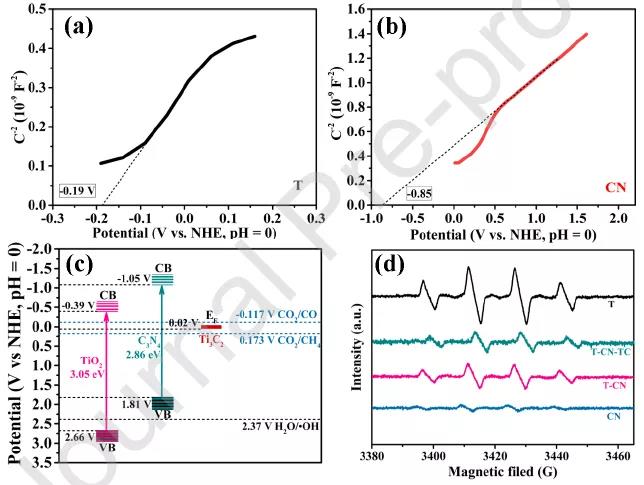
Figure 6 MS diagram.
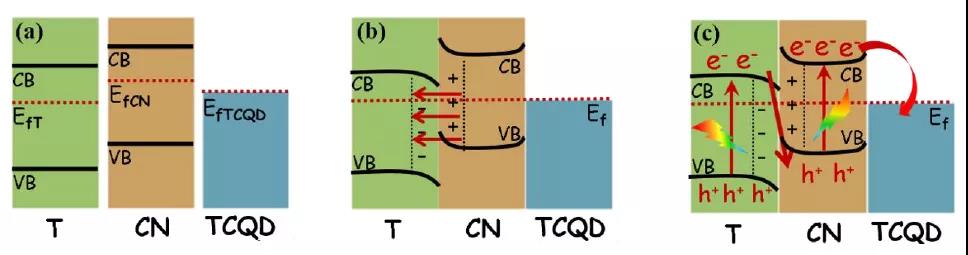
Figure 7 Segmented charge transfer mechanism.
in conclusion
In short, a unique two-dimensional van der Waals heterojunction was prepared by self-assembly at the interface of TCQD modified TiO 2 / C 3 N 4 core-shell nanosheets. The yields of CO and CH4 obtained after reduction of CO 2 are 3 times and 8 times that of TiO 2 and C 3 N 4 , respectively . The results show that the s -type heterojunction at the TiO 2 / C 3 N 4 interface and the Schottky heterojunction at the C 3 N 4 / TCQD interface play a major role in the catalytic process. This work provides a reasonable structural design strategy for the regulation of the number and type of heterojunctions.
Original link:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926337320304215
Source: MXene Academic
This information originates from the Internet for academic exchange only. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it immediately











