As an emerging two-dimensional nanomaterial, MXene has received extensive attention from researchers in interdisciplinary fields such as materials science in recent years. In the content of the previous issues, the editor has compiled and introduced the current research status of MXene through WOS data (there is a link at the end of the article). Coincidentally, the top journal of materials science, Adv. Funct. Mater. (IF 15.621), was recently published in the special issue of MXene, which includes three reviews, a progress report, and four research papers to show everyone the progress made by the MXene Institute. The 8 articles covered multiple research fields, and the relevant authors have made progress in different research fields of MXene. Next, the editor will give you a brief introduction.
【Review & Progress report】
1. Song Li & Chen Shuangming, China University of Science and Technology: MXene surface control and interlayer engineering
MXene has a unique layered structure and surface chemistry, which is an important factor for providing good application prospects for MXene. In fact, by controlling the surface functional groups and the interlayer spacing, the internal characteristics of MXene are highly adjustable. In addition, synchrotron radiation X-ray characterization has great potential for exploring the relationship between the properties and structure of MXene. In particular, in-situ X-ray testing can help us better understand the dynamics of MXene-based energy storage materials. In this review, Professor Song Li and Associate Researcher Chen Shuangming from the University of Science and Technology of China made a comprehensive summary of the latest research on MXene‘s surface control, interlayer engineering and MXene-based synchronous acceleration technology characterization. At the same time, the prospects of MXene and related advanced X-ray characterization technologies were also discussed.

Figure 1. Schematic diagram of MXene preparation, surface control, interlayer engineering, and corresponding synchrotron radiation characterization
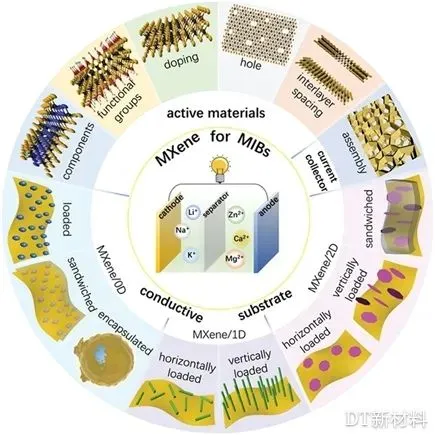
2. Professor Wu Zhongshuai, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics: Research progress of MXene-based nanostructured materials in metal ion batteries
In recent years, MXene as a metal ion battery electrode material has shown good application prospects. Its excellent electrical conductivity, surface functional groups, low energy barrier to diffusion of metal ions, and large interlayer spacing for ion insertion provide a good opportunity to build a metal ion battery (MIB) with high energy density and power density . Therefore, the research group of Professor Wu Zhongshuai of Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics reviewed the latest progress of MXene-based nanostructures for high-performance MIBs. From lithium ion battery systems to non-lithium ion (Na + , K + , Mg 2+ , Zn 2+ , Ca 2+ ) ion battery systems, MXenes has been shown whether it is used as an active material, a conductive substrate, or a current collector Good application prospects. In addition, the authors start from different hybridization methods (loading, coating, sandwich structure) for MXene-based hybrid materials containing active materials of different dimensions (0D, 1D, and 2D). Between MXene and active materials in different MIB systems The synergy and reaction interface are elaborated. Finally, the author also briefly discussed the challenges and research prospects of MXene-based nanostructured materials.

Figure 2. Application of MXene-based nanostructured materials in different MIB systems
3. Wang Jing & Li Laisheng of South China Normal University: MXene-based photothermal conversion nanomaterials
In addition to its advantages in electrochemical energy storage, MXenes has also shown good application prospects in the field of photothermal conversion in recent years. MXene has excellent electromagnetic wave absorption capability and local surface plasmon resonance effect, thus showing good light-to-heat conversion performance. Light-to-heat conversion is an effective method of using solar energy. It can convert solar energy into heat energy, so that MXenes can be used in various fields, such as solar energy conversion steam and biomedicine. However, so far, little attention has been paid to the photothermal function of MXenes. In this article, the author summarizes the latest progress of MXene photothermal conversion to fully understand its photothermal conversion mechanism and application. First, the author briefly outlines the synthesis strategy of MXenes and its nanocomposites, and then discusses the latest developments in photothermal conversion mechanisms and photothermal applications.

Figure 3. Schematic diagram of MXene photothermal conversion
4. KIST & Chong Min Koo University: Progress in electromagnetic shielding research based on 2D MXene
Since the first research report on electromagnetic shielding (EMI) of 2D Ti 3 C 2 T x in 2016 , MXenes has excellent shielding performance, excellent metal conductivity, low density, large specific surface area, adjustable surface Chemical properties and processability of the solution. MXenes has aroused great interest in the material research community. In the past three years, there have been more than 100 reports on the electromagnetic shielding of MXenes. To further improve the EMI shielding performance of MXene, the researchers studied and reported MXene-based composite / hybrid materials based on different microstructures: such as laminated sheet structure, layer-by-layer self-assembly structure, porous foam / aerogel, and isolation structure Wait. Experiments show that different structures do cause differences in the electromagnetic shielding performance of the materials. This article comprehensively reviews the latest progress of MXene-based electromagnetic shielding materials with different structural forms, thus providing guidance for solving the current challenges of electromagnetic shielding materials.

Figure 4. MXene based electromagnetic shielding materials research trends
【Full Paper】
In addition to the above review articles, this issue of AFM has also published a number of research papers on MXene online, including: 1. Professor Sun Zhengming & Associate Professor Zhang Wei of Southeast University Theory combined with experiments on nitrogen-doped Ti 3 C 2 MXene system Research; 2. Professor Xu Bin of Beijing University of Chemical Technology used in-situ ice template method to prepare flexible MXene film for high performance supercapacitors; 3. Yohan Dall‘Agnese of University College London & Gao Yu of Jilin University & Yury Gogotsi of Drexel University Three teams of flexible Nb 4 C 3 T x thin films with large layer spacing are used in high-performance supercapacitors; 4. Beihang Professor Sun Zhimei & Associate Professor Zhou Jian: Two-dimensional transition metal carbides with high efficiency electrocatalytic properties for full hydrolysis And ORR. Due to space limitations, the editor will not introduce it in detail here. Interested students can read the original document through the link at the end of the article.
【to sum up】
In recent years, the research of MXene has become a hot spot in the field of materials, and this special issue of Adv. Funct. Mater. Also shows us the good research and application prospects of MXene in many fields such as energy storage, light-to-heat conversion, electromagnetic shielding and so on. At the same time, research based on MXene also faces many challenges. I believe that research in this field will make great progress with the solution of one problem after another.
【references】
1.Tuning 2D MXenes by Surface Controlling and Interlayer Engineering: Methods, Properties, and Synchrotron Radiation Characterizations. Changda Wang, Shuangming Chen, Li Song. DOI: 10.1002 / adfm.202000869
2.Recent Advances and Promise of MXene‐Based Nanostructures for High‐Performance Metal Ion Batteries. Yanfeng Dong, Haodong Shi, Zhong‐Shuai Wu. DOI: 10.1002 / adfm.202000706
3.Insights into the Photothermal Conversion of 2D MXene Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Mechanism, and Applications. Dingxin Xu, Zhidong Li, Laisheng Li, Jing Wang. DOI: 10.1002 / adfm.202000712
4.2D MXenes for Electromagnetic Shielding: A Review. Aamir Iqbal, Pradeep Sambyal, Chong Min Koo. DOI: 10.1002 / adfm.202000883
5.Nitrogen-Doped Ti 3 C 2 MXene: Mechanism Investigation and Electrochemical Analysis. Chengjie Lu, Li Yang, Bingzhen Yan, Liangbo Sun, Peigen Zhang, Wei Zhang, ZhengMing Sun. DOI: 10.1002 / adfm.202000852
6.In Situ Ice Template Approach to Fabricate 3D Flexible MXene Film‐Based Electrode for High Performance Supercapacitors. Peng Zhang, Qizhen Zhu, Razium A. Soomro, Shiyu He, Ning Sun, Ning Qiao, Bin Xu. DOI: 10.1002 / adfm. 202000922
7. Flexible Nb 4 C 3 T x Film with Large Interlayer Spacing for High‐Performance Supercapacitors. Shuangshuang Zhao, Chaofan Chen, Xin Zhao, Xuefeng Chu, Fei Du, Gang Chen, Yury Gogotsi, Yu Gao, Yohan Dall‘Agnese. DOI : 10.1002 / adfm.202000815
8.Novel 2D Transition‐Metal Carbides: Ultrahigh Performance Electrocatalysts for Overall Water Splitting and Oxygen Reduction. Yadong Yu, Jian Zhou, Zhimei Sun. DOI: 10.1002 / adfm.202000570
This information originates from the Internet for academic exchange only. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it immediately








