|
Metal organic framework (MOF) is one of the best materials for catalysis, gas storage and gas storage and processing. So far, more than 20,000 different MOFs have been manufactured and characterized.
|
|
“Although MOF is produced in loose powder form and tested on a laboratory scale, applications often require solids that are easy to handle and have a specific shape and sufficient mechanical strength to withstand long-term destructive pressures such as wear and hydrostatic pressure "Jérémy Dhainaut is a researcher at the Catalyze et Chimie du Solide Joint Research Center (UCCS) at the University of Lille (he was a postdoctoral researcher at the Kyoto University Institute of Integrated Cellular Materials Science (WPI-iCeMS)) ). "In our recent work, we have focused on the preparation of MOF-based solids by mechanical casting with controlled macroscopic morphology and excellent texture characteristics."
|
|
The key issue in designing MOF-based solids is to find the best combination of material porosity and mechanical resistance relevant to a particular application.
|
|
As the team reported in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces ( "Formulation of Metal Organic Frame Inks for High-Pressure Gas Solid Storage and Separation with High-Pressure Solid 3D Printing" ), they used an improved 3D printer to control ink deposition (HKUST-1, CPL-1 , ZIF-8 , and UiO-66-NH four different MOF powder 2 ) in the presence of a low proportion of binder and plasticizer in the preparation .
|
|
"This automatic casting is a micro-paste technology, which is a micro-extrusion technology based on the controlled layer-by-layer deposition of paste. Its advantage is that it can well control the size and shape of the final solid, and the effect is very limited. Porosity ", Dhainaut explained. "In the presence of a small amount of cellulose-derived binder, the solid not only self-sustains after drying, but also exhibits corresponding firmness."
|
|
He pointed out that few technologies can meet all these conditions at the same time, so it is particularly suitable for a wide range of applications.
|
|
|
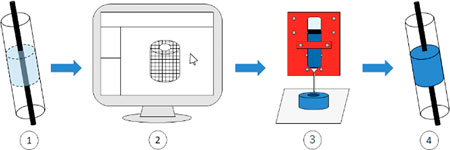
Typical process workflow based on the method developed here: (1) Determining requirements; (2) Computer-aided modeling for fitting solids; (3) MOF-based ink deposition using 3D printers; and (4) Solid performance evaluation . (Reprinted with permission from the American Chemical Society)
|
|
All characterization techniques indicate that the 3D printing process will only have a slight impact on the structure and structural characteristics of the MOF, and it has comparable performance to gas storage powders (carbon dioxide, methane, and separation powder), which is promising for future applications. (Ethylene / ethane).
|
|
Indeed, the solid exhibits permanent micropores comparable to the original powder. They also have higher compressive strength, only 1-2 orders of magnitude lower than dense binderless pellets.
|
|
Generally, when the porous powder is formed, the performance will be reduced due to too much binder, which will hinder the entry or densification process of the pores, thereby partially destroying the pore network. In particular, MOF is composed of elements (metal clusters and organic compounds) that are weakly bonded to each other.
|
|
"Previous studies have shown that when the densification technology used on an industrial scale is applied to MOF, it leads to irreversible performance loss," Dhainaut said. "This is not the case when using our automated broadcast technology."
|

|
|
Under the same conditions, photographs of CPL-1 based objects printed with ink formulated with CPL-1 containing 35 wt% (a) and 51 wt% (b) (Reprinted with permission from the American Chemical Society) (click on the image to enlarge)
|
|
The team‘s results are still preliminary, and some improvements need to be implemented before developing actual applications.
|
|
For example, they plan to print more viscous paste to increase the loading of MOF powder, thereby improving the final robustness and volume absorption (the volume of gas that a specific volume of material can absorb). 3D printing materials.
|
|
Moreover, they will soon start printing more porous powders, which are more fragile, but will significantly increase the weight absorption rate of the final material (the weight of gas that a specific weight of material can absorb).
|
|
The US Department of Energy has set a high volume and weight absorption rate, which is a prerequisite for hydrogen and natural gas vehicles, and the use of the same material rarely meets both requirements.
|
|
Dhainaut concluded: "We believe that our research paves the way for the preparation of highly porous MOF-based solids and that its design is fully suitable for its application: microreactors, adsorption beds or separation membranes with specific morphologies, to name a few. "
Source: Nanowerk
|





