已传文件:photo/1631586161.png
Article information
Grafted MXene/polymer electrolyte is used to extend the shelf life of zinc batteries at high/low temperature First author: Chen Ze, Li Xinliang Corresponding author: Zhi Chunyi* Unit: City University of Hong Kong
Research Background
Aqueous zinc ion batteries (ZIBs) have always been considered as a new type of energy storage device with great potential due to their high safety and competitive capacity. However, as far as the practical application of ZIBs is concerned, its shelf life is difficult to meet the requirements, mainly because there are inevitable side reactions between the aqueous electrolyte and zinc metal, including corrosion, hydrogen evolution and passivation. These undesirable side reactions result in an abnormal increase in the interface impedance of the battery, which reduces the utilization rate of the zinc anode, and ultimately severely reduces the shelf life of ZIBs. The use of all-solid electrolytes can efficiently solve the above problems, because a series of side reactions of water molecules in the system are completely avoided. However, there are few reports on solid electrolytes in ZIBs, and high-performance zinc-electric solid electrolytes have yet to be developed.
Article Introduction
Based on this, the team of Professor Chunyi Zhi from City University of Hong Kong published a research paper entitled Grafted MXene/Polymer Electrolyte for High Performance Solid Zinc Batteries with Enhanced Shelf Life at Low/High Temperatures in Energy Environ. Sci. Poly(methyl acrylate) grafted MXenes filled poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) (PVHF/MXene-g-PMA) solid polymer electrolyte (SPE) is used to solve the problem of low shelf life of ZIBs.
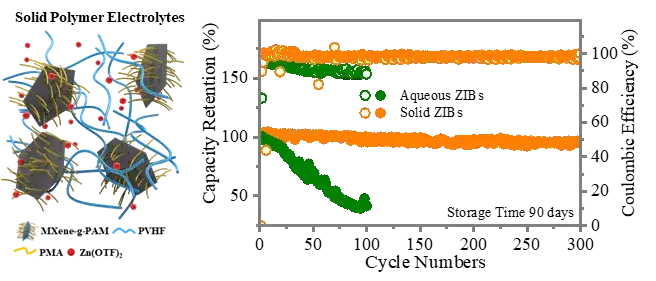
Figure 1. The composition of a polymer solid electrolyte based on grafted Mxene and the electrochemical performance of an ordinary aqueous electrolyte and the solid electrolyte after a certain period of storage.
Highlights of this article
Point 1: The solid electrolyte with high zinc ion mobility through the interaction between PMA and PVHF polymer, the grafted MXenes can be uniformly dispersed in the matrix. The results show that the ionic conductivity of the SPE at room temperature is 3 orders of magnitude higher than that of the ordinary PVHF matrix, reaching 2.69×10-4 S cm-1, which can be increased by another order of magnitude at high temperatures. Based on this electrolyte, highly reversible dendrite-free galvanizing/stripping is realized, which can be circulated for more than 1000 hours at room temperature and more than 200 hours at high temperature. Point 2: All-solid-state zinc batteries with high shelf life
Key point 2: All solid-state zinc batteries with high shelf life, which can eliminate HER and inhibit negative Zn dendrites, exhibit excellent cycle performance of up to 10,000 cycles at room temperature, and can be in the temperature range of -35 to 100 ℃ normal work. The most important thing is that the shelf life of all-solid ZIBs exceeds 90 days regardless of whether it is at low or high temperatures. This research has made substantial progress in all-solid-state ZIBs with excellent stability and reliability, which effectively inhibited zinc dendrites and side reactions, achieved excellent cycle performance and significant shelf life.
Article link
Grafted MXene/Polymer Electrolyte for High-Performance Solid Zinc Batteries with Enhanced Shelf Life at Low/High Temperatureshttps://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2021/ee/d1ee00409c#!divAbstract
This information is sourced from the Internet for academic exchanges only. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it immediately.